1601 Geometry Made Simple
题目描述
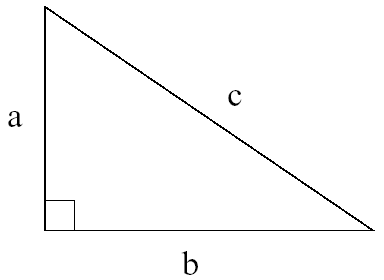
Mathematics can be so easy when you have a computer. Consider the following example. You probably know that in a right-angled triangle, the length of the three sides a, b, c (where c is the longest side, called the hypotenuse) satisfy the relation a*a+b*b=c*c. This is called Pythagora's Law.
Here we consider the problem of computing the length of the third side, if two are given.
输入格式:
The input contains the descriptions of several triangles. Each description consists of a line containing three integers a, b and c, giving the lengths of the respective sides of a right-angled triangle. Exactly one of the three numbers is equal to -1 (the 'unknown' side), the others are positive (the 'given' sides).
A description having a=b=c=0 terminates the input.
输出格式:
For each triangle description in the input, first output the number of the triangle, as shown in the sample output. Then print "Impossible." if there is no right-angled triangle, that has the 'given' side lengths. Otherwise output the length of the 'unknown' side in the format "s = l", where s is the name of the unknown side (a, b or c), and l is its length. l must be printed exact to three digits to the right of the decimal point.
Print a blank line after each test case.
3 4 -1 -1 2 7 5 -1 3 0 0 0
Triangle #1 c = 5.000 Triangle #2 a = 6.708 Triangle #3 Impossible.
